Essential Guide to Small Business Finance
A practical guide to small business finance covering cash flow management, budgeting, funding options, debt control, and financial planning to support sustainable growth.
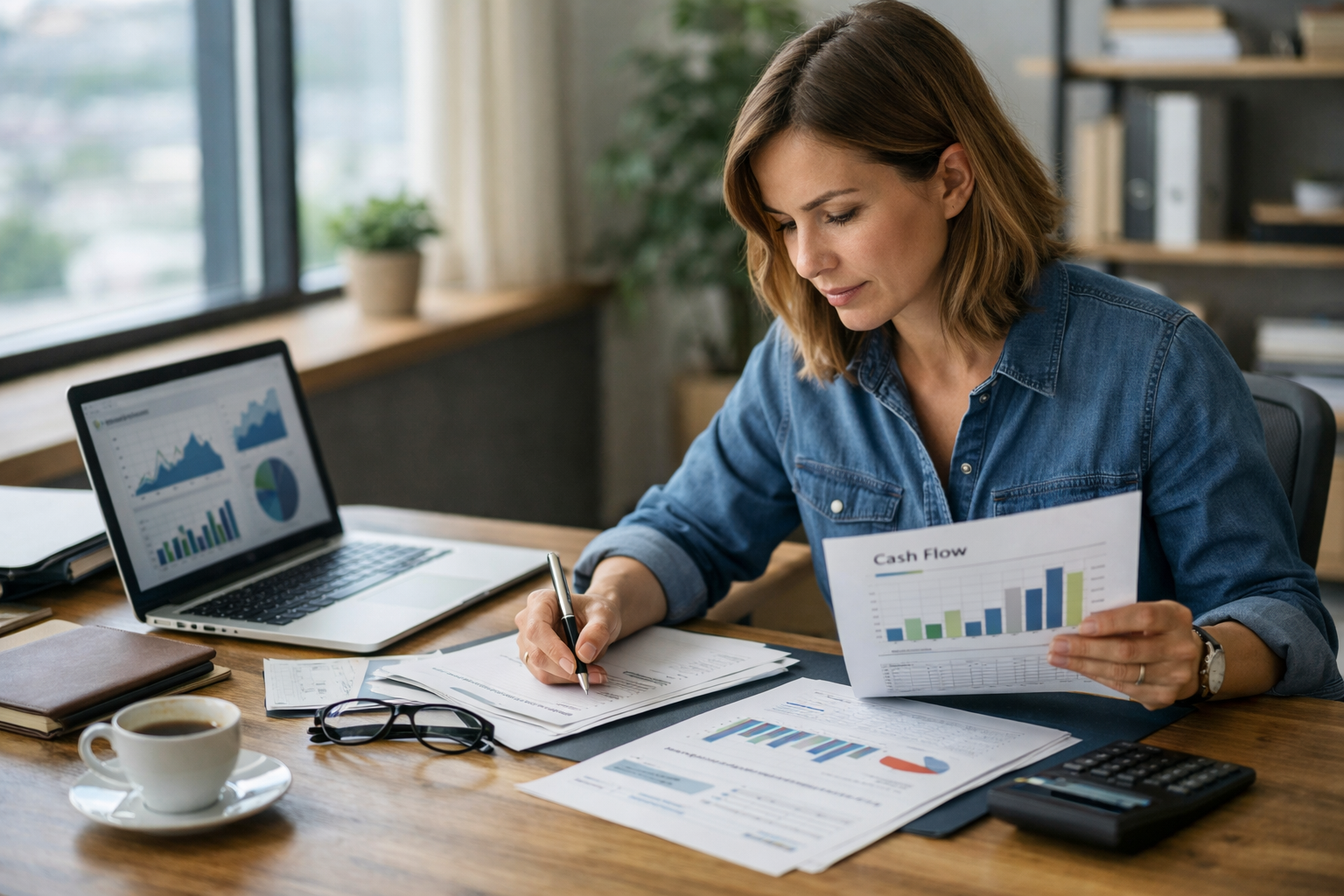
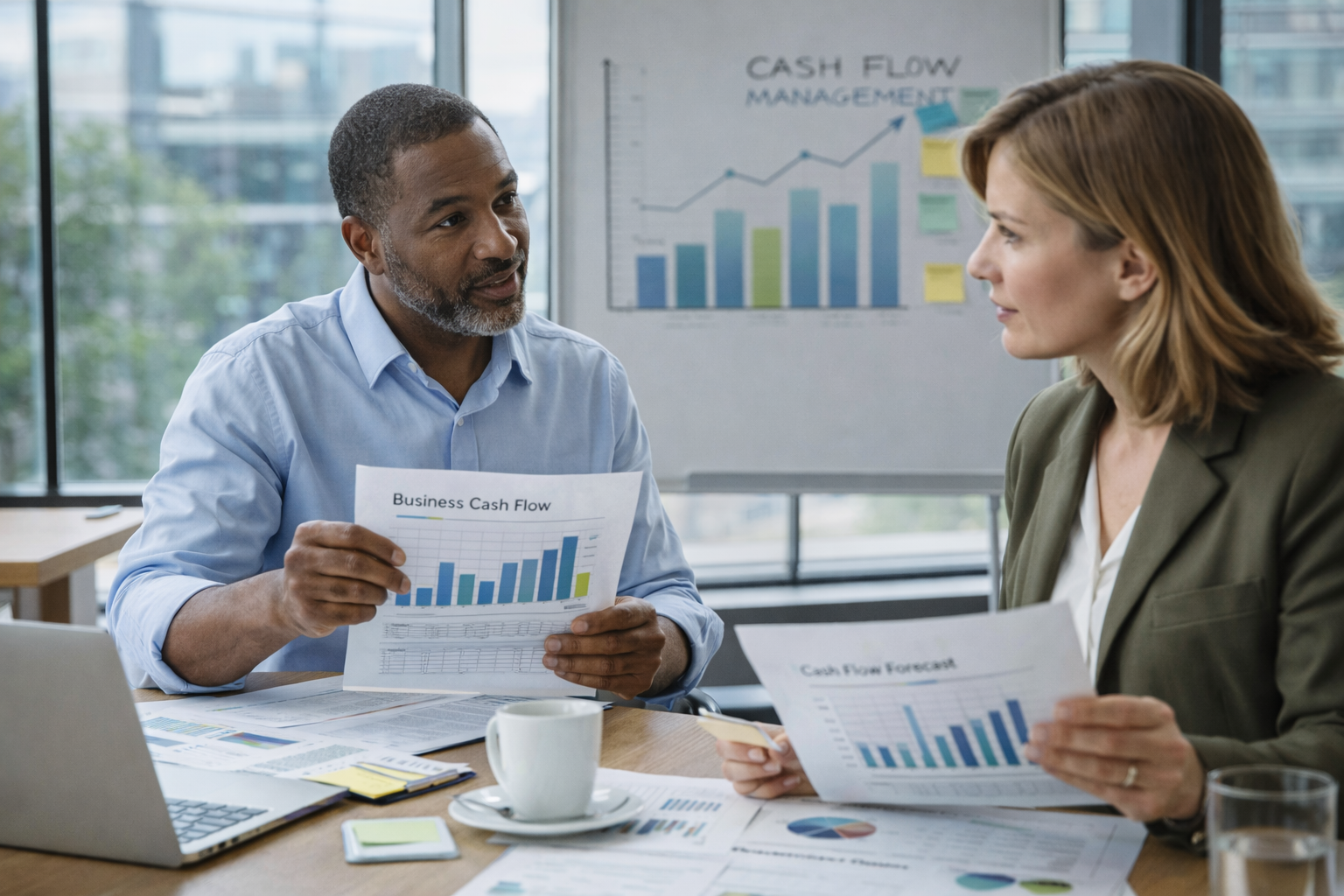
Managing finances effectively is one of the most critical factors determining whether a small business survives, scales, or fails. While innovation and market demand drive growth, financial discipline sustains it. From cash flow management to funding strategy, understanding the fundamentals of small business finance is no longer optional, it is a competitive advantage.
This guide outlines the core financial principles every small business owner needs to master.
1. Understanding Cash Flow: The Lifeblood of Any Business
Profit does not equal cash. Many profitable businesses fail due to poor cash flow management.
Cash flow refers to the movement of money in and out of a business. Expenses such as payroll, rent, inventory, and taxes must be paid on time, regardless of when revenue is collected.
Key best practices include:
- Monitoring cash flow weekly or monthly
- Maintaining a cash buffer for unexpected costs
- Aligning payment terms with operational needs
- Avoiding over-reliance on delayed receivables
Strong cash flow discipline allows businesses to remain agile during economic uncertainty.
2. Budgeting and Financial Planning
A budget is not a constraint, it is a strategic tool.
Effective budgeting helps business owners:
- Forecast revenue and expenses
- Identify cost inefficiencies
- Allocate resources toward growth opportunities
- Prepare for seasonal fluctuations
Financial planning should extend beyond short-term budgeting. A rolling 12–24 month financial forecast provides visibility into future risks and funding needs, enabling proactive decision-making rather than reactive cost-cutting.
3. Managing Costs Without Sacrificing Growth
Cost control is essential, but indiscriminate cost-cutting can damage long-term performance.
Successful small businesses distinguish between:
- Fixed costs (rent, salaries, insurance)
- Variable costs (inventory, marketing spend, logistics)
Regular expense reviews help identify areas where spending does not generate proportional value. At the same time, strategic investments, such as technology, talent, or customer acquisition, should be protected if they contribute to sustainable growth.
4. Financing Options for Small Businesses
Access to capital remains one of the biggest challenges for small businesses. Choosing the right financing method depends on growth stage, risk tolerance, and cash flow stability.
Common options include:
- Bootstrapping through retained earnings
- Bank loans and credit lines
- Government-backed financing programs
- Angel investors and venture capital
- Revenue-based financing
- Trade credit and supplier financing
Each option carries different implications for ownership, repayment obligations, and financial flexibility. Businesses should align financing decisions with long-term strategy, not short-term pressure.
5. Debt Management and Credit Health
Debt can accelerate growth, or amplify risk.
Responsible debt management involves:
- Matching debt maturity to asset lifespan
- Avoiding excessive leverage
- Monitoring interest rate exposure
- Maintaining a strong credit profile
A healthy credit history improves access to financing and reduces borrowing costs, particularly during economic tightening cycles.
6. Financial Reporting and Key Metrics
Timely, accurate financial reporting is essential for informed decision-making.
Core financial statements include:
- Income statement (profit and loss)
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
Beyond reports, small business owners should track key performance indicators such as:
- Gross margin
- Operating margin
- Customer acquisition cost
- Lifetime customer value
- Working capital ratio
These metrics provide early warning signals long before financial stress becomes visible.
7. Tax Planning and Compliance
Tax mismanagement is a common and costly mistake.
Effective tax planning involves:
- Understanding applicable tax obligations
- Setting aside reserves for tax payments
- Taking advantage of legitimate deductions and incentives
- Working with qualified accountants or tax advisors
Proactive tax planning improves cash flow predictability and reduces regulatory risk.
8. Preparing for Growth and Uncertainty
As a business grows, financial complexity increases. Systems that worked at an early stage may no longer scale.
Preparation includes:
- Upgrading financial systems and controls
- Separating personal and business finances
- Establishing internal financial governance
- Stress-testing the business against downturn scenarios
Resilient businesses plan not only for growth, but for volatility.
Final Thought
Small business finance is not about mastering spreadsheets, it is about making informed, disciplined decisions that protect the business while enabling growth. Entrepreneurs who understand their numbers gain clarity, confidence, and control over their future.
In an increasingly competitive and uncertain global economy, financial literacy is one of the most powerful tools a small business can possess.
Comments 0
Most Read
Recommended Post
Top U.S. Lawmaker Accuses DOJ of Cover-Up in Jeffrey Epstein Files
Lindsey Graham’s Rhetoric Fuels Chaos While He Denies Responsibility



















Leave a Comment